Building a CI/CD pipeline for a Node.js app with Docker and Jenkins
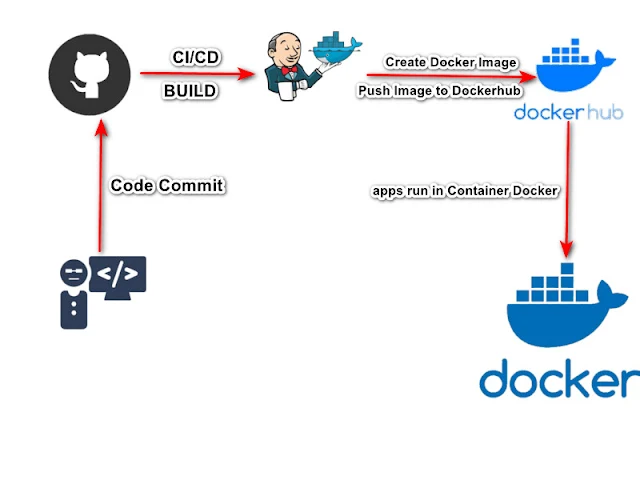
So, you've got this fantastic Node.js app, and now you're thinking, "How can I make the development and deployment process smoother than a freshly paved road?" Well, my friend, the answer lies in creating a robust CI/CD pipeline using Docker and Jenkins. Buckle up, because we're about to embark on a journey of automation and efficiency!
What's CI/CD, Anyway?
Before we dive in, let's quickly chat about CI/CD. CI stands for Continuous Integration, where code changes from multiple contributors are automatically merged into a shared repository. CD, on the other hand, expands to Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment, ensuring that your code is always in a deployable state.
Step 1: Setting Up Jenkins
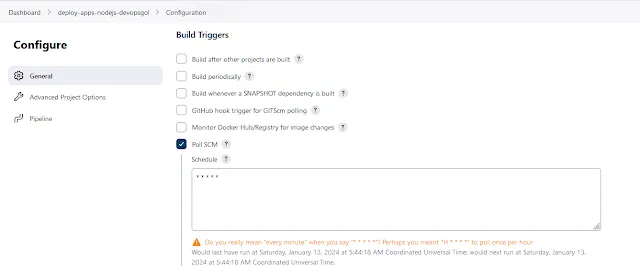
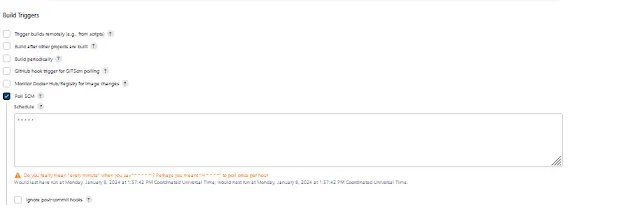
First things first, let's get Jenkins up and running. Install Jenkins on your server, and don't forget to grab some coffee while you wait. Once Jenkins is installed, access the web interface and set up your pipelines. you can see the guide install jenkins
Articel related : Setup Jenkins on Kubernetes
Step 2: Dockerizing Your Node.js App
Time to containerize! Create a Dockerfile for your Node.js app, specifying the base image, dependencies, and commands to run your app. Docker makes your app independent of the environment, ensuring consistency across different stages of your pipeline.
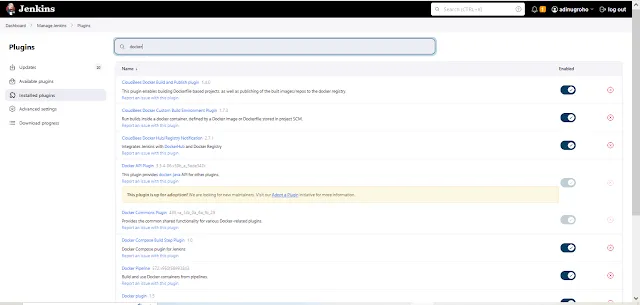
Articel related : How to Setup Docker Containers as Build Agents for Jenkins
Create a Docker file for apps dockerized
Here, I use my project github link : node-dockerized-projects
Step 3: Jenkins Pipeline Configuration
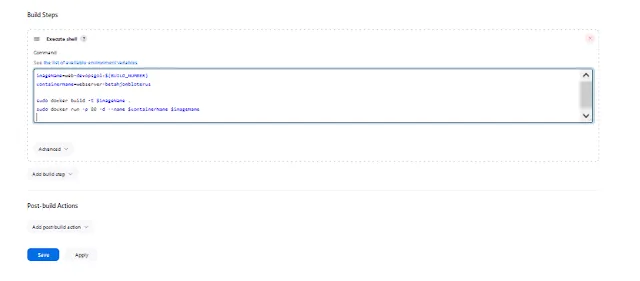
Now, let's tell Jenkins what to do. Create a Jenkinsfile in your project repository, defining the stages of your pipeline. This file will be your guiding light for Jenkins, ensuring it knows how to build, test, and deploy your app.
In a Jenkins pipeline, Groovy code is typically defined in a Jenkins file, which is a text file containing the pipeline definition. Jenkins files are written in the Groovy programming language and are used to define stages, phases, and other components of a process.
There are many stages checkout, test,build, build image, docker push to docker hub and docker run
1. Stage CheckOut
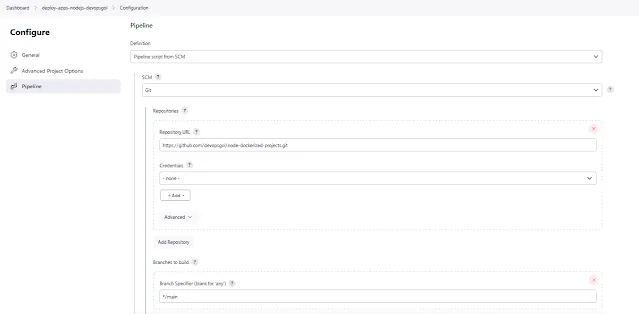
In a jenkins pipelines the checkout stage is stage use fetch form version control system (SCM).SCM. Here, i use Github as my version control system ( SCM).
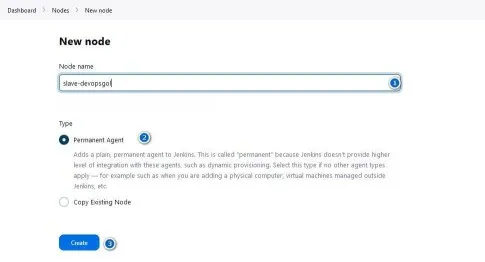
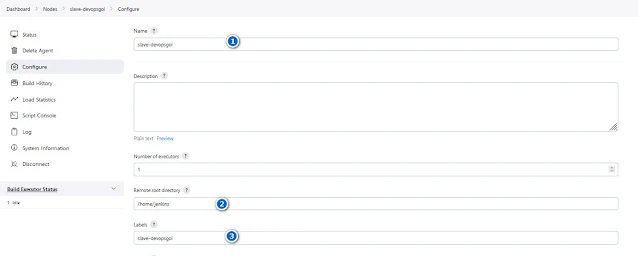
In pipelines, in the agent section, you can specify the agent node. If you're using a remote Docker host to deploy a Node.js application, you can refer to the guide on adding a Docker agent in Jenkins. Like the slave-devopsgol
In Jenkins pipelines, the testing stages include installing npm packages for requirements.
In the build stage of NPM, it runs Node.js apps using the command npm run build.
The "Build" step can encompass all the necessary actions to compile the code, package it in a usable format, and perform other required preparation tasks.
In the stages section, "Build push to docker hub" carries out the task of pushing the generated Docker image from the Build Image stage to Docker Hub.
In the "docker run" stage, it runs the container that has been pushed to Docker Hub, using port 3000 as the exposed port according to the Dockerfile.
Complete Pipelines Jenkinsfile
Details for a jenkinsfile deploy application simple nodejs. Sure, I can certainly check out the source code on the GitHub link you provided : https://github.com/devopsgol/node-dockerized-projects.git
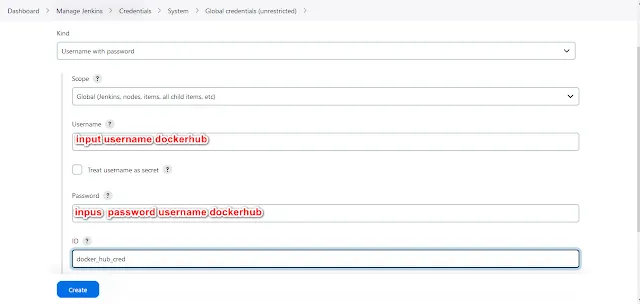
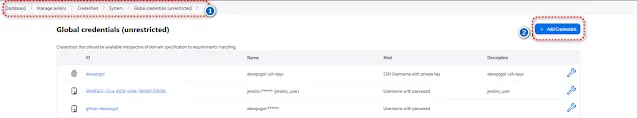
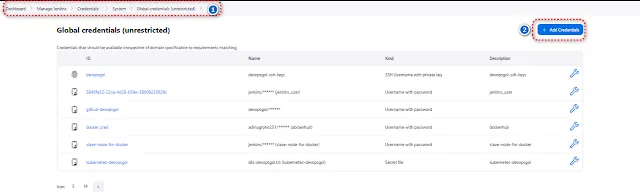
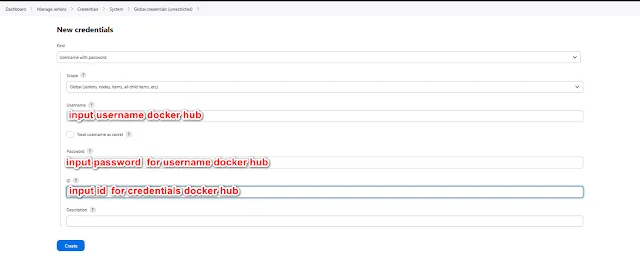
Step 4: Docker Registry Credentials
To push your Docker image to a registry, you'll need credentials. In Jenkins, go to "Manage Jenkins" > "Manage Credentials" > "Jenkins" > "Global credentials" and add your Docker Hub or any other registry credentials.
Articel Related : HOW TO INTEGRATION OF SLACK NOTIFICATIONS WITH JENKINS
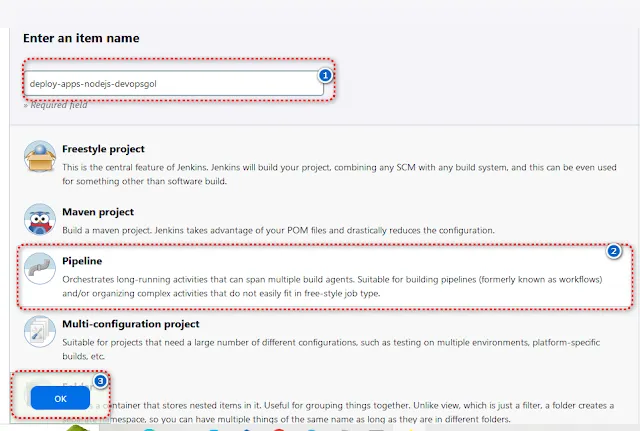
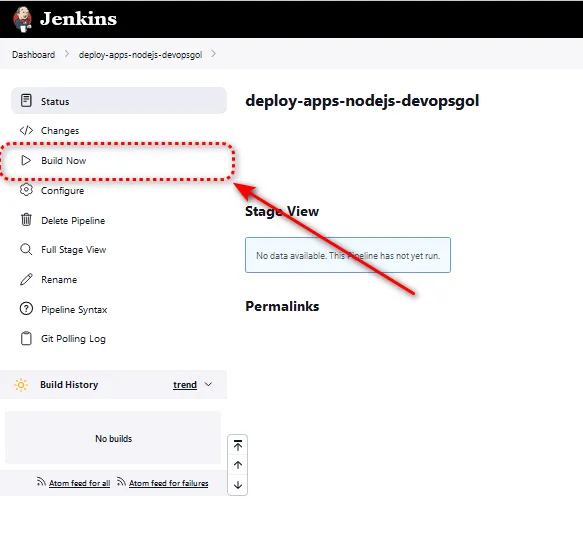
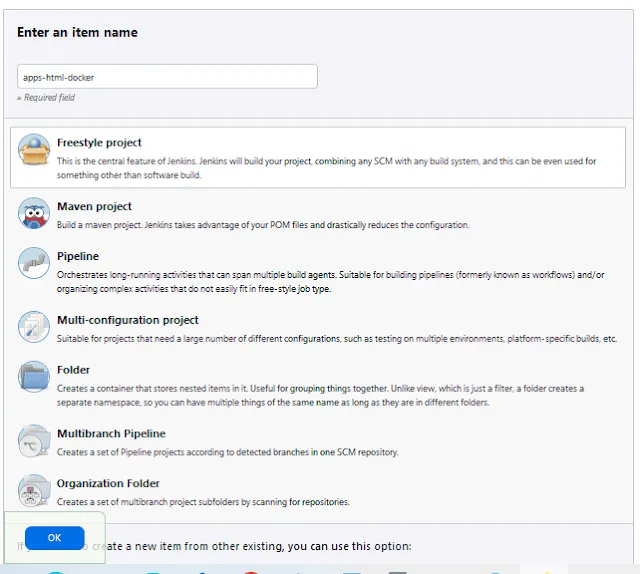
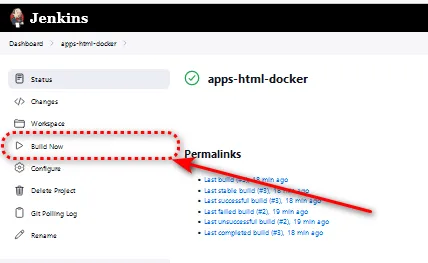
Step 5: Run Your Pipeline in jenkins
Once you've finished generating the Dockerfile and Jenkinsfile steps, now you can create job pipelines to execute that Jenkinsfile.
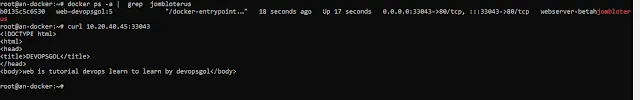
Well's running container for docker remote host and test curl port apps node.js is running well's
Conslusion
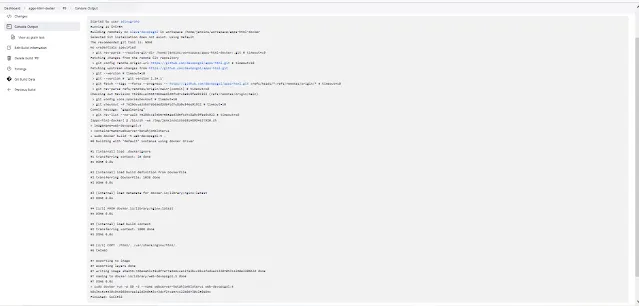
It's showtime! Trigger your Jenkins pipeline and watch the magic happen. Jenkins will fetch your code, build, test, and deploy it in a seamless flow. Sit back and enjoy the automation symphony!
Congratulations, you've just built a CI/CD pipeline for your Node.js app using Docker and Jenkins. Now, every code change will go through this automated process, ensuring reliability and speed in your development lifecycle. Happy coding! 🚀