How to Setup Docker Containers as Build Agents for Jenkins
In the realm of DevOps,
orchestrating seamless workflows is imperative, and Jenkins, with its
extensibility, stands out as a powerhouse.
In this comprehensive tutorial,
we will delve into the integration of Docker and SSH for Jenkins agents,
providing a step-by-step guide to enhance your CI/CD pipelines. You can see the previous guide, namely setup Jenkins on Kubernetes
Prerequisites
Before embarking on this journey,
ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
1.
A Jenkins server up and running.
2.
Docker installed on both the Jenkins server and
the machine you intend to use as a Docker host.
3.
SSH access configured between the Jenkins server
and the Docker host.
4.
Java should be installed on your agent server.
Step 1: Set Up Jenkins
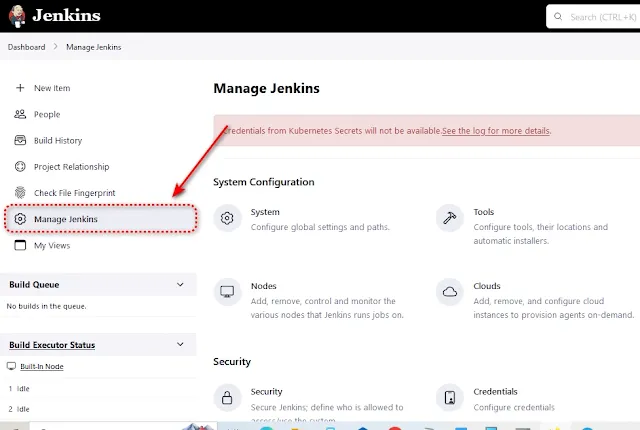
Open your Jenkins dashboard and
navigate to "Manage Jenkins."
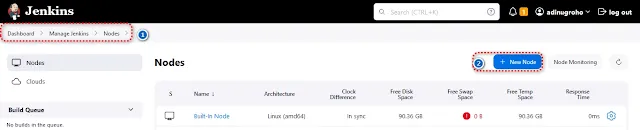
Click on "Manage Nodes "
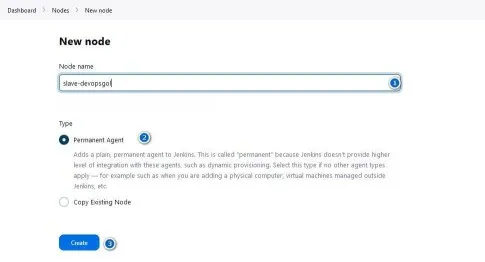
Select "New Node" to
create a new Jenkins agent.
Provide a name for the agent and choose "Permanent
Agent."
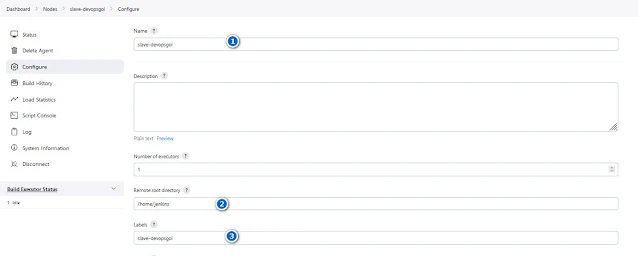
In the configuration, specify the following:
• Remote
root directory: Choose a directory on the Docker host where Jenkins agents will
be launched.
• Labels:
Assign labels to the agent for identification.
Related Article : HOW TO INSTALL AND USE DOCKER : Getting Beginner
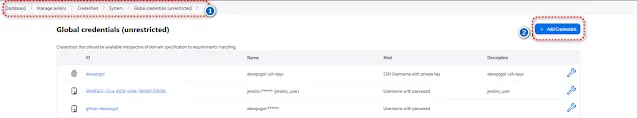
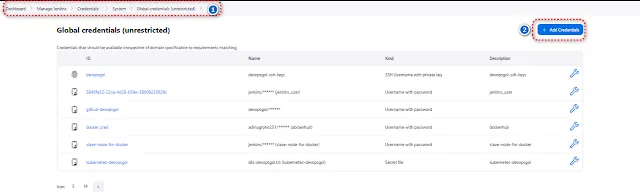
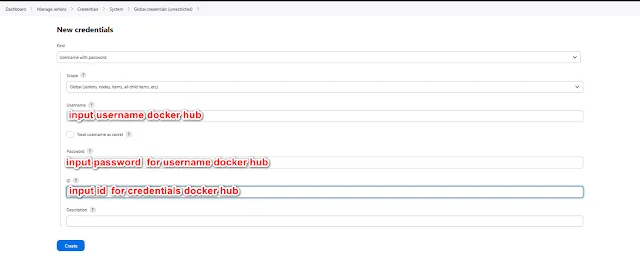
Select Manage Jenkins --> Credentials --> system --> Global unrestricted --> add credentials
Input the ip addres of the docker host
- Usage : Select Usage this is node much as possible for node ssh
- Lauch Method : Select agent ssh for add node docker with ssh agent
- Host : Input IP ADDRESS OR Hostname Docker Host
- Credentials : Select Credentials for docker host.
Save the configuration.
Related Articel : How to Install Kubernetes on Ubuntu 20.04
Step 2 : Create user jenkins and install java for docker host
Add user jenkins in docker host
Add entri file below this paragraph in visudo
Install package java for requiretment jenkins agent
Verify java version
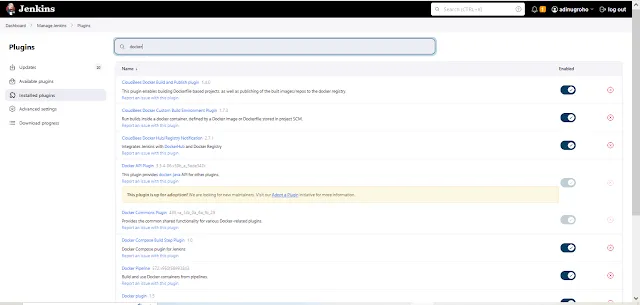
Step 3 : Install Docker Plugin
In the Jenkins dashboard, navigate to "Manage Jenkins" > "Manage Plugins." >> Select Plugins --> Install
Select Plugin this below :
CloudBees Docker Build and Publish plugin Version 1.4.0
CloudBees Docker Custom Build Environment Plugin Version 1.7.3
CloudBees Docker Hub/Registry Notification Version 2.7.1
Docker
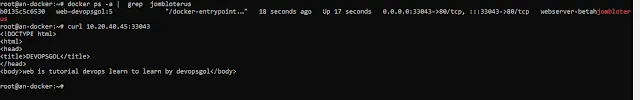
Step 4: CI/CD : Automation Deploy Application HTML Using Jenkins
Fantastic! Adding a Docker node is a great step. Now, let's dive into deploying that simple HTML application via Jenkins. Here's a brief guide for you:
Prerequisites
- Docker Hub
- Jenkins Server is running
- Dockerfile
- Jenkinsfile
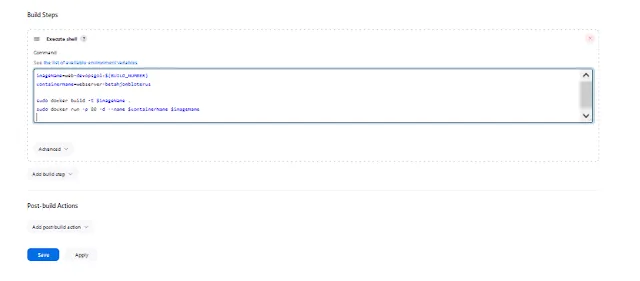
Example Dockerfile
Example Jenkinsfile
For detail projects simple html : https://github.com/devopsgol/apps-html
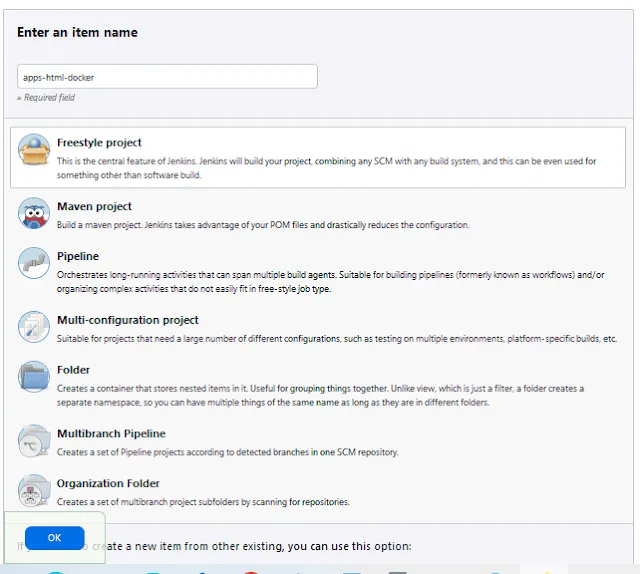
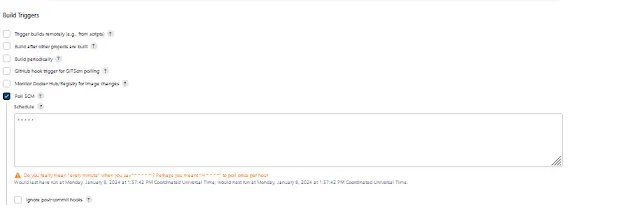
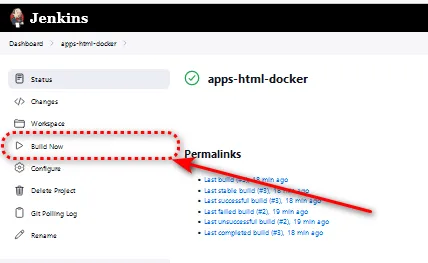
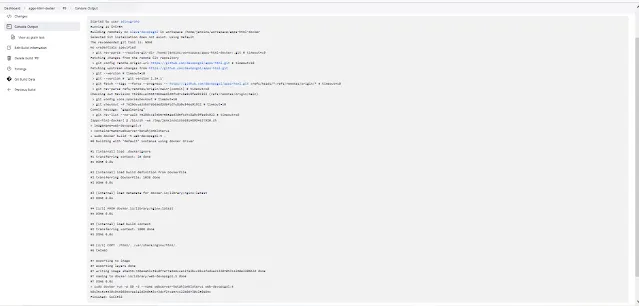
Add Job in Jenkins for CI/CD
Conlusion
Congratulations! You have
successfully integrated Docker and SSH for Jenkins agents, enhancing the
scalability and flexibility of your CI/CD pipelines.
If you want to read more
insightful tutorials and articles related to DevOps, feel free to visit The
Insider's Views.